Rich Heritage Of Turkish Ethnicity: A Deep Dive Into Culture And Traditions
The concept of Turkish ethnicity evokes a rich tapestry of history, culture, and traditions that have shaped the identity of millions of people. This ethnic group, primarily associated with the Republic of Turkey, is known for its diverse cultural influences that have come from centuries of migration, conquest, and trade. The Turks are mainly of Central Asian origin but have intermingled with people from various regions, leading to a unique cultural amalgamation that defines Turkish ethnicity today.
Rooted in an extensive history that dates back to the nomadic tribes of Central Asia, Turkish ethnicity has evolved through interactions with major civilizations such as the Byzantine, Roman, and Ottoman Empires. These interactions have left an indelible mark on the Turkish people, contributing to a vibrant culture that encompasses language, religion, art, and cuisine. The Turks have managed to preserve their distinct identity while embracing elements from the cultures they have encountered over the centuries.
Present-day Turkish ethnicity is a reflection of a complex history that has seen the rise and fall of empires, the spread of Islam, and the modernization efforts of the 20th century. It is characterized by a strong sense of national pride and cultural heritage, as well as a commitment to preserving traditions in a rapidly changing world. This article will delve into the various aspects of Turkish ethnicity, exploring its history, cultural practices, social structures, and more, providing a comprehensive understanding of what it means to be Turkish today.
Read also:Sir Knowles A Tribute To A Legendary Icon In The World
Table of Contents
- Historical Background of Turkish Ethnicity
- Language and Dialect: The Linguistic Richness
- What Are the Religious Beliefs of Turkish Ethnicity?
- Cultural Practices and Traditions
- How is the Family Structure in Turkish Ethnicity?
- Art and Literature: Turkish Contributions
- Turkish Cuisine: A Culinary Journey
- What Role Does Music and Dance Play in Turkish Culture?
- Modern Influences on Turkish Ethnicity
- Education and Core Values
- Ethnic Diversity within Turkey
- Impact of Globalization on Turkish Ethnicity
- The Turkish Diaspora: Spreading the Legacy
- Efforts in Preserving Turkish Cultural Heritage
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Historical Background of Turkish Ethnicity
Turkish ethnicity has its roots in the ancient tribes of Central Asia, particularly the region known as the Turkic Khaganate. These tribes were known for their nomadic lifestyle, moving across vast areas of land and establishing trade routes that connected different parts of Asia. Over time, the Turks migrated westward, eventually settling in what is now modern-day Turkey. This migration was marked by various interactions with other civilizations, including the Byzantine and Roman Empires.
The most significant period in the history of Turkish ethnicity was the rise of the Ottoman Empire. This empire, which lasted from the late 13th century to the early 20th century, was one of the largest and most influential in history. It played a crucial role in shaping the cultural and social structures of Turkish ethnicity. The Ottoman period was characterized by a blend of Turkish, Islamic, and European influences, which are still evident in the cultural practices of Turkey today.
The Ottoman Legacy
The Ottoman Empire left a lasting legacy on Turkish ethnicity, with its influence seen in areas such as architecture, language, and governance. The Ottoman sultans were patrons of the arts, leading to a flourishing of literature, music, and visual arts. They also established a complex system of administration that laid the foundation for modern Turkish governance.
Republican Era and Modernization
Following the decline of the Ottoman Empire, the Republic of Turkey was established in 1923 under the leadership of Mustafa Kemal Atatürk. This period marked a significant transformation in Turkish ethnicity, as Atatürk introduced sweeping reforms to modernize the country. These reforms included the adoption of the Latin alphabet, the promotion of secularism, and the encouragement of Western-style education and cultural practices.
Language and Dialect: The Linguistic Richness
The Turkish language is a member of the Turkic language family, which includes languages spoken in regions such as Central Asia, the Middle East, and Eastern Europe. Modern Turkish is derived from Ottoman Turkish, which was heavily influenced by Arabic and Persian. Atatürk's language reforms in the 1920s led to the purification of the Turkish language, reducing the number of foreign loanwords and standardizing grammar and vocabulary.
Today, Turkish is the official language of Turkey and is spoken by the majority of the population. It is characterized by its agglutinative structure, meaning that words are formed by adding suffixes to a root word. This allows for a high degree of expressiveness and flexibility in the language.
Read also:Mastering The Strategy How To Get Endorsement Level 5 Effortlessly
Dialects and Regional Variations
While standard Turkish is widely spoken, there are several regional dialects that reflect the linguistic diversity within Turkey. These dialects can vary significantly in terms of pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar. Notable dialects include the Aegean, Black Sea, and Eastern Anatolian dialects, each with its own unique characteristics.
Language and Identity
The Turkish language plays a crucial role in shaping the identity of Turkish ethnicity. It serves as a unifying factor among the diverse ethnic groups within Turkey, fostering a sense of national pride and cultural cohesion. Language is also an important tool for preserving cultural heritage, with traditional proverbs, songs, and stories passed down through generations in Turkish.
What Are the Religious Beliefs of Turkish Ethnicity?
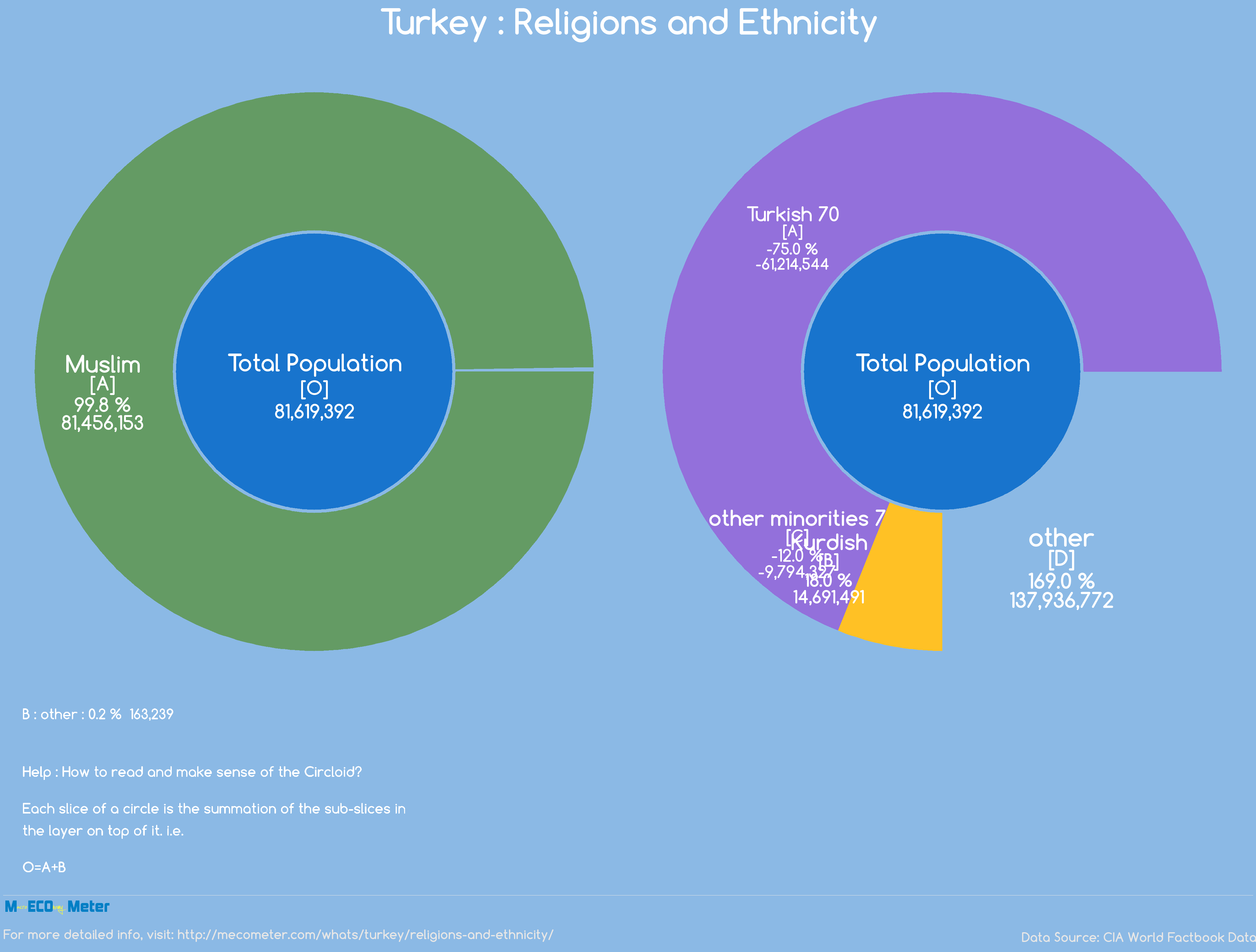
Religion plays a central role in the cultural and social life of Turkish ethnicity. The majority of Turks identify as Sunni Muslims, following the Hanafi school of Islamic jurisprudence. Islam was introduced to the region during the Seljuk and Ottoman periods, and it has since become deeply integrated into the cultural fabric of Turkish society.
In addition to Sunni Islam, there are also significant populations of Alevi Muslims, who follow a distinct interpretation of Islam that incorporates elements of Sufism and Shi'ism. The Alevi community is known for its emphasis on spiritualism, music, and poetry, with rituals that differ from those of Sunni Muslims.
Religious Practices and Festivals
Religious practices among Turkish ethnicity include daily prayers, fasting during the month of Ramadan, and the celebration of Islamic festivals such as Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha. These festivals are marked by communal prayers, feasting, and acts of charity, reflecting the values of hospitality and generosity that are central to Turkish culture.
Secularism and Modernization
While religion remains an important aspect of Turkish ethnicity, the establishment of the Republic of Turkey brought about a shift towards secularism. Atatürk's reforms aimed to separate religion from state affairs, leading to the establishment of a secular government and legal system. This secularization has influenced the way religion is practiced in Turkey, with a greater emphasis on personal spirituality and freedom of belief.
Cultural Practices and Traditions
The cultural practices and traditions of Turkish ethnicity are a vibrant reflection of its rich history and diverse influences. These practices encompass a wide range of activities, from traditional arts and crafts to social customs and rituals.
One of the most iconic elements of Turkish culture is its art of carpet weaving. Turkish carpets, known for their intricate designs and vibrant colors, are considered masterpieces of craftsmanship and have been prized for centuries. The tradition of carpet weaving is passed down through generations, with each region of Turkey producing distinct styles and patterns.
Social Customs and Etiquette
Social customs and etiquette play a significant role in Turkish society, emphasizing values such as hospitality, respect, and community. Turks are known for their warm and welcoming nature, often inviting guests into their homes and offering them tea or coffee as a gesture of friendship. Hospitality is considered a sacred duty, and Turks take pride in ensuring that their guests feel comfortable and well-cared for.
Traditional Clothing and Attire
Traditional clothing is another important aspect of Turkish ethnicity, with garments that vary based on region, occasion, and social status. The most distinctive item of traditional Turkish attire is the fez, a cylindrical hat that was once a symbol of Ottoman identity. While modern Turks typically wear Western-style clothing, traditional garments are still worn on special occasions and religious festivals.
How is the Family Structure in Turkish Ethnicity?
The family is the cornerstone of Turkish society, playing a vital role in social organization and cultural identity. Turkish families are traditionally extended, with multiple generations living under one roof and sharing responsibilities. This structure fosters a strong sense of unity and support, with family members relying on one another for assistance and guidance.
Within Turkish families, respect for elders is of utmost importance, and younger generations are expected to show deference to their parents and grandparents. This respect is reflected in everyday interactions, with children addressing their elders using formal titles and expressions of politeness.
Gender Roles and Dynamics
Gender roles in Turkish families have traditionally been defined by cultural norms, with men serving as the primary breadwinners and women taking on domestic responsibilities. However, these roles are evolving, with increasing numbers of Turkish women pursuing education and careers outside the home. This shift has led to changes in family dynamics, with more egalitarian relationships emerging between men and women.
Marriage and Family Life
Marriage is a significant milestone in Turkish culture, often celebrated with elaborate ceremonies and rituals. Weddings are typically large gatherings that bring together family and friends, featuring music, dancing, and feasting. Arranged marriages were once common in Turkey, but modern Turks increasingly choose their own partners, with love marriages becoming the norm.
Art and Literature: Turkish Contributions
Turkish art and literature are rich and diverse, reflecting the country's complex history and cultural influences. The artistic heritage of Turkish ethnicity includes a wide range of forms, from traditional calligraphy and miniature painting to modern sculpture and digital art.
Turkish literature dates back to the 8th century, with the Orkhon inscriptions providing some of the earliest examples of written Turkic language. Over the centuries, Turkish literature has evolved, with notable contributions from poets such as Yunus Emre and Fuzuli, as well as novelists like Orhan Pamuk, who won the Nobel Prize in Literature in 2006.
Visual Arts and Craftsmanship
The visual arts have long been an integral part of Turkish culture, with a focus on intricate designs and detailed craftsmanship. Traditional art forms such as tilework, ceramics, and metalwork continue to thrive, with artisans creating pieces that are both functional and beautiful. The art of calligraphy, particularly Arabic script, is also highly regarded in Turkish culture, often used to decorate religious texts and architectural elements.
Contemporary Art and Innovation
In recent years, contemporary Turkish artists have gained international recognition for their innovative approaches to art. These artists often explore themes related to identity, politics, and globalization, using a variety of mediums to express their ideas. Istanbul, in particular, has become a hub for contemporary art, hosting numerous galleries and exhibitions that showcase the work of both established and emerging artists.
Turkish Cuisine: A Culinary Journey
Turkish cuisine is a testament to the country's diverse cultural influences and culinary traditions. It is characterized by a rich variety of flavors, ingredients, and cooking techniques, with dishes that are both hearty and flavorful.
One of the most well-known elements of Turkish cuisine is its use of spices and herbs, which add depth and complexity to dishes. Common spices include cumin, paprika, and sumac, while fresh herbs such as parsley, mint, and dill are often used to garnish and flavor meals.
Signature Dishes and Ingredients
Some of the most iconic dishes in Turkish cuisine include kebabs, dolma (stuffed grape leaves), and baklava, a sweet pastry made with layers of filo dough, nuts, and honey. Turkish cuisine also features a wide range of mezes, or small appetizers, that are served before the main course. These dishes often include items such as hummus, baba ghanoush, and stuffed peppers.
Beverages and Desserts
Turkish tea and coffee are staples of the national diet, often enjoyed throughout the day as a social activity. Tea is typically served in small, tulip-shaped glasses, while Turkish coffee is known for its strong flavor and thick consistency. Desserts play a significant role in Turkish cuisine, with sweets such as Turkish delight and baklava enjoyed during special occasions and celebrations.
What Role Does Music and Dance Play in Turkish Culture?
Music and dance are integral components of Turkish culture, serving as expressions of identity and tradition. Turkish music is characterized by its diversity, with influences from Central Asia, the Middle East, and the Balkans, resulting in a unique blend of sounds and styles.
Traditional Turkish music includes a variety of genres, such as folk music, classical music, and religious music. Folk music, in particular, is deeply rooted in the daily lives and customs of the Turkish people, often telling stories of love, heroism, and nature.
Instruments and Melodies
Turkish music features a wide range of instruments, including the saz (a stringed instrument similar to a lute), the ney (a type of flute), and the darbuka (a type of drum). These instruments are used to create complex melodies and rhythms, often accompanied by vocal performances that highlight the emotional depth of the music.
Dance Forms and Celebrations
Dance is another important aspect of Turkish culture, with traditional dances performed at weddings, festivals, and other social gatherings. These dances often involve intricate footwork, rhythmic movements, and colorful costumes, reflecting the cultural diversity of Turkey. Popular dance forms include the Halay, a folk dance performed in a circle, and the Zeybek, a solo dance that symbolizes bravery and heroism.
Modern Influences on Turkish Ethnicity
The 20th and 21st centuries have brought significant changes to Turkish ethnicity, as the country has undergone rapid modernization and globalization. These changes have influenced various aspects of Turkish culture, from fashion and technology to social norms and values.
One of the most notable modern influences on Turkish ethnicity is the rise of technology and digital media. The internet and social media platforms have connected Turks with people from around the world, leading to the exchange of ideas and cultural practices. This connectivity has also provided a platform for young Turks to express their creativity and individuality, contributing to the evolution of Turkish identity.
Urbanization and Lifestyle Changes
The migration of people from rural areas to cities has also impacted Turkish ethnicity, leading to changes in lifestyle and social dynamics. Urbanization has brought about greater access to education, healthcare, and economic opportunities, but it has also resulted in the loss of some traditional customs and practices. Despite these changes, many Turks remain committed to preserving their cultural heritage, finding ways to adapt traditional practices to modern life.
Globalization and Cultural Exchange
Globalization has facilitated cultural exchange between Turkey and other countries, leading to the incorporation of foreign elements into Turkish culture. This exchange has enriched Turkish ethnicity, with new influences seen in areas such as fashion, cuisine, and entertainment. At the same time, Turks have taken pride in sharing their own cultural heritage with the world, showcasing the richness and diversity of Turkish ethnicity on the global stage.
Education and Core Values
Education is highly valued in Turkish society, with a strong emphasis on academic achievement and personal development. The Turkish education system is based on a centralized model, with the Ministry of National Education overseeing the curriculum and standards for schools across the country.
Turkish education places a strong emphasis on subjects such as mathematics, science, and literature, as well as the teaching of Turkish language and history. In recent years, there has been a growing focus on the importance of critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills, reflecting the needs of a rapidly changing world.
Core Values and Ethical Principles
In addition to formal education, Turkish society places a strong emphasis on the development of core values and ethical principles. These values include respect for others, honesty, responsibility, and a commitment to family and community. Education is seen as a means of instilling these values in young people, helping them to become responsible and productive members of society.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the strengths of the Turkish education system, there are challenges that need to be addressed, such as disparities in access to quality education between urban and rural areas. Efforts are being made to improve educational opportunities for all Turks, with initiatives focused on expanding access to technology, improving teacher training, and promoting lifelong learning.
Ethnic Diversity within Turkey
While Turkish ethnicity is the dominant cultural group in Turkey, the country is home to a diverse population that includes various ethnic and cultural minorities. This diversity is a reflection of Turkey's strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, which has made it a melting pot of cultures and peoples.
Some of the largest ethnic minorities in Turkey include the Kurds, Arabs, Circassians, and Armenians, each with its own unique cultural practices and traditions. These groups contribute to the richness of Turkish culture, adding to the country's linguistic, religious, and artistic diversity.
The Role of Ethnic Minorities
Ethnic minorities in Turkey play an important role in shaping the country's cultural landscape, with contributions to areas such as music, cuisine, and art. Efforts are being made to promote the rights and cultural heritage of these groups, ensuring that their voices are heard and their traditions are preserved.
Challenges and Integration
While Turkey's ethnic diversity is a source of strength, it also presents challenges in terms of social integration and cohesion. Efforts are being made to promote unity and understanding among different ethnic groups, fostering a sense of belonging and shared identity. These efforts include initiatives focused on education, cultural exchange, and dialogue, which aim to bridge gaps and build a more inclusive society.
Impact of Globalization on Turkish Ethnicity
Globalization has had a profound impact on Turkish ethnicity, influencing various aspects of culture, economy, and society. The increased interconnectedness of the world has led to the exchange of ideas, goods, and services, creating new opportunities and challenges for Turkish people.
One of the most significant impacts of globalization on Turkish ethnicity is the spread of Western cultural influences. These influences are seen in areas such as fashion, entertainment, and consumer behavior, with many Turks adopting Western-style clothing, music, and lifestyle habits. At the same time, Turks have also sought to preserve their cultural heritage, finding ways to integrate traditional practices with modern trends.
Economic Implications
Globalization has also had economic implications for Turkey, with increased trade and investment leading to economic growth and development. This growth has created new opportunities for Turks, but it has also led to challenges such as income inequality and environmental concerns. Efforts are being made to address these challenges, with a focus on sustainable development and inclusive economic policies.
Preserving Cultural Identity
Amidst the changes brought about by globalization, Turks remain committed to preserving their cultural identity and heritage. This commitment is reflected in efforts to promote traditional arts and crafts, support local industries, and encourage cultural exchange. By balancing tradition and modernity, Turkish ethnicity continues to thrive in a rapidly changing world.
The Turkish Diaspora: Spreading the Legacy
The Turkish diaspora refers to the millions of people of Turkish descent living outside of Turkey, primarily in Europe, North America, and the Middle East. This diaspora has played a significant role in spreading Turkish culture and traditions around the world, contributing to the global appreciation of Turkish ethnicity.
Migration from Turkey to other countries has been driven by various factors, including economic opportunities, political instability, and family reunification. As a result, Turkish communities have established themselves in countries such as Germany, the United States, and the Netherlands, where they have become an integral part of the multicultural landscape.
Cultural Exchange and Influence
The Turkish diaspora has facilitated cultural exchange between Turkey and other countries, with Turkish traditions and practices influencing areas such as cuisine, music, and art. This exchange has enriched both Turkish and host cultures, creating a dynamic and diverse cultural tapestry.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the Turkish diaspora has contributed to the spread of Turkish culture, it also faces challenges related to integration and identity. Many Turks living abroad strive to maintain their cultural heritage while adapting to the norms and values of their host countries. Efforts are being made to support these communities, promoting cultural exchange, education, and dialogue to foster understanding and inclusivity.
Efforts in Preserving Turkish Cultural Heritage
Preserving cultural heritage is a priority for Turkish ethnicity, with efforts focused on safeguarding traditional practices, historical sites, and artistic expressions. These efforts are driven by a commitment to maintaining the cultural identity and legacy of Turkish people for future generations.
One of the key initiatives in preserving Turkish cultural heritage is the protection of historical sites and monuments. Turkey is home to numerous ancient sites, including the ruins of Ephesus, the Hagia Sophia, and the Cappadocia region, which attract millions of visitors each year. Efforts are being made to preserve these sites, ensuring that they remain intact and accessible to future generations.
Promoting Traditional Arts and Crafts
Traditional arts and crafts are an essential aspect of Turkish cultural heritage, with efforts focused on promoting and supporting artisans and craftsmen. This includes initiatives to provide training and resources for artists, as well as opportunities to showcase their work at exhibitions and festivals.
Cultural Education and Awareness
Cultural education plays a vital role in preserving Turkish heritage, with programs aimed at raising awareness and appreciation for traditional practices and values. These programs are often implemented in schools and communities, helping to instill a sense of pride and identity in young Turks.
Conclusion
Turkish ethnicity is a rich and diverse tapestry of culture, history, and traditions that have evolved over centuries. From its roots in Central Asia to its modern-day expression in Turkey and beyond, Turkish ethnicity is a testament to the resilience and adaptability of its people. Despite the challenges posed by globalization and modernization, Turks remain committed to preserving their cultural heritage while embracing new influences and opportunities.
This commitment is reflected in the vibrant cultural practices, artistic expressions, and social structures that define Turkish ethnicity. By balancing tradition and modernity, Turks continue to thrive in a rapidly changing world, sharing their rich heritage with the global community and contributing to the multicultural landscape of the 21st century.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the origin of Turkish ethnicity?
Turkish ethnicity originated from the nomadic tribes of Central Asia, particularly the Turkic Khaganate. These tribes migrated westward and eventually settled in the region that is now modern-day Turkey.
- What language do Turkish people speak?
Turkish people primarily speak the Turkish language, which is a member of the Turkic language family. It is the official language of Turkey and is characterized by its agglutinative structure.
- What are some traditional Turkish dishes?
Traditional Turkish dishes include kebabs, dolma, baklava, and a variety of mezes such as hummus and baba ghanoush. Turkish cuisine is known for its use of spices and herbs, adding depth and complexity to its flavors.
- How does Turkish ethnicity promote cultural preservation?
Turkish ethnicity promotes cultural preservation through initiatives focused on safeguarding historical sites, supporting traditional arts and crafts, and raising cultural awareness through education and community programs.
- What role does religion play in Turkish culture?
Religion plays a central role in Turkish culture, with the majority of Turks identifying as Sunni Muslims. Religious practices and festivals, such as Ramadan and Eid al-Fitr, are important aspects of Turkish social and cultural life.
- How has globalization impacted Turkish ethnicity?
Globalization has influenced various aspects of Turkish ethnicity, from fashion and entertainment to economic growth and cultural exchange. While it has brought new opportunities, Turks remain committed to preserving their cultural heritage amidst these changes.
For more information about Turkish culture and history, you can visit the Cultural Turkey website.
Celebrity Appearances On Barney: The Behind-the-Scenes Story
Rhode Island FC Players: A Deep Dive Into Their Journey And Impact
Remarkable Cast Of Crossfire Trail: A Closer Look At The Talented Ensemble

Full ethnicity map of turkish counties r/AngryObservation
Religions and Ethnicity Turkey