Where Was Gaul? The Historical Landscape And Its Legacy
Gaul was an ancient region of Western Europe that played a pivotal role in shaping the political and cultural landscape of what is now modern-day France and parts of neighboring countries. Known for its rich history, Gaul was inhabited by Celtic tribes before becoming a significant part of the Roman Empire. The region's strategic importance, diverse cultures, and eventual integration into the Roman world have left an indelible mark on European history.
Understanding where Gaul was located geographically and its historical significance requires delving into its past and exploring the various factors that made it a center of attention for many ancient civilizations. From its tribal societies to the Roman conquest and beyond, Gaul's story is one of transformation and adaptation. This article will take you through the historical landscape of Gaul, examining its origins, the people who lived there, and the impact it had on the ancient world.
The legacy of Gaul continues to influence contemporary culture and identity. Its history is not just a tale of conquest and integration but also a testament to the resilience and adaptability of its people. As we explore the various aspects of Gaul's history, geography, and culture, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of a region that was once a cornerstone of the ancient world.
Read also:Experience The Magic Your Guide To Primavera Barcelona Festival 2024
Table of Contents
- Geographical Location of Gaul
- Who Were the Gauls?
- What Was the Significance of Gaul in Ancient Times?
- Roman Conquest of Gaul
- How Did the Roman Rule Impact Gaul?
- Cultural Legacy of Gaul
- Economy and Trade in Gaul
- Religion and Beliefs of the Gauls
- Gaulish Language and Literature
- Where Was Gaul in the Context of the Roman Empire?
- Decline of Roman Gaul
- How Did Gaul Influence Modern Europe?
- Archaeological Discoveries in Gaul
- Gaul in Popular Culture
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
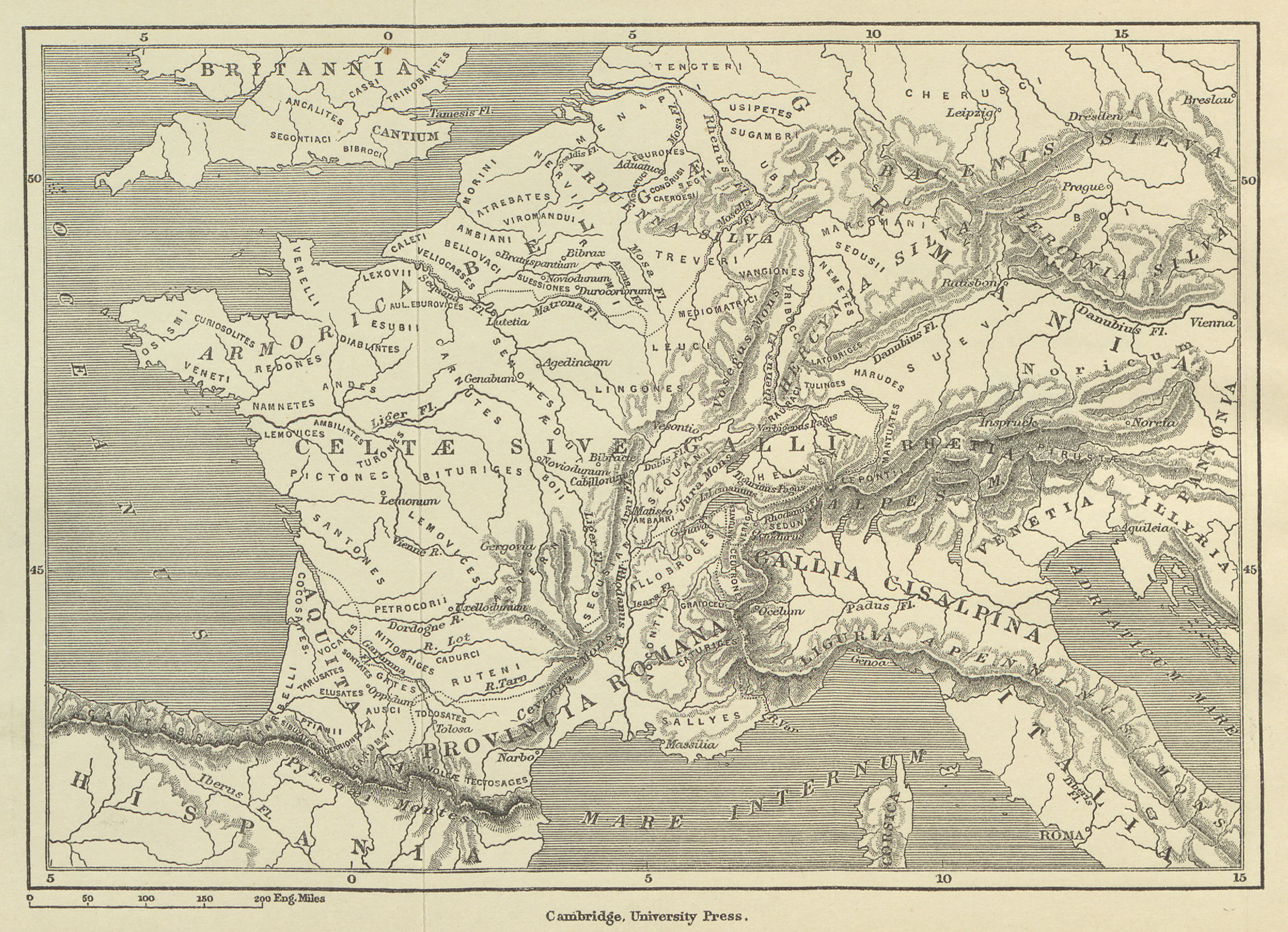
Geographical Location of Gaul
The geographical expanse of Gaul covered a significant portion of Western Europe. It primarily consisted of what is now modern-day France, but its boundaries also extended into parts of Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, and Northern Italy. The natural borders of Gaul were largely defined by the Rhine River to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Pyrenees Mountains to the south, and the English Channel to the northwest.
The diverse landscape of Gaul included dense forests, fertile plains, and mountainous regions, making it a rich and varied environment for the tribes that inhabited it. The geography of Gaul played a crucial role in its historical development, influencing settlement patterns, trade routes, and military strategies. The region was well-positioned as a crossroads between the Mediterranean cultures and the northern European tribes, contributing to its significance in ancient times.
Throughout history, the strategic location of Gaul made it a target for conquest and colonization. Its fertile lands and abundant resources attracted various peoples, from the Celts who initially settled there to the Romans who saw it as a valuable addition to their empire. Understanding the geographical scope of Gaul is essential to comprehending its historical importance and the role it played in shaping the ancient world.
Who Were the Gauls?
The Gauls were a group of Celtic tribes that inhabited the region known as Gaul. They were known for their warrior culture, complex social structures, and vibrant artistic traditions. The Gauls spoke a Celtic language and were closely related to other Celtic peoples across Europe, sharing cultural and linguistic similarities.
Gaulish society was tribal in nature, with each tribe occupying a specific territory within the region. These tribes were often in conflict with each other, but they also formed alliances for mutual protection and cooperation. The social hierarchy within Gaulish tribes was well-defined, with a ruling class of nobles, a warrior class, and commoners. Druids, who served as religious leaders and advisors, played a significant role in Gaulish society, wielding considerable influence over both spiritual and political matters.
Despite their reputation as fierce warriors, the Gauls were also skilled artisans and traders. They engaged in trade with neighboring regions, exchanging goods such as metalwork, textiles, and ceramics. The Gauls' craftsmanship and artistry are evident in the archaeological finds from the region, showcasing their talents in metalworking, pottery, and sculpture. Understanding who the Gauls were provides insight into the cultural and social dynamics of the region before the Roman conquest.
Read also:Cardi B Age All You Need To Know About The Rappers Journey
What Was the Significance of Gaul in Ancient Times?
Gaul held significant importance in ancient times due to its strategic location, abundant resources, and cultural influence. The region served as a crucial link between the Mediterranean world and the northern European tribes, facilitating trade and cultural exchange. Its fertile lands and natural resources made it an attractive territory for conquest and settlement.
The strategic position of Gaul allowed it to play a key role in the expansion of the Roman Empire. The conquest of Gaul by Julius Caesar in the 1st century BCE marked a turning point in the region's history, integrating it into the Roman world and transforming its social, political, and economic structures. The Romanization of Gaul brought about significant changes, including the introduction of Roman law, architecture, and urban planning.
In addition to its geopolitical significance, Gaul was also a center of cultural and artistic innovation. The Celts of Gaul contributed to the rich tapestry of European culture through their art, music, and mythology. Their influence can be seen in the development of various artistic and cultural movements across Europe. The significance of Gaul in ancient times lies in its ability to bridge diverse cultures and facilitate the exchange of ideas and knowledge.
Roman Conquest of Gaul
The Roman conquest of Gaul was a monumental event in the history of the region, marking the end of Gaulish independence and the beginning of a new era of Roman influence. The conquest began in 58 BCE under the leadership of Julius Caesar, who sought to expand Roman territory and secure his political power within the Roman Republic.
The Gallic Wars, as they are known, were a series of military campaigns waged by Caesar against the various tribes of Gaul. These campaigns were characterized by strategic brilliance, brutal warfare, and complex alliances. Caesar's success in Gaul was largely due to his ability to exploit tribal rivalries and employ advanced Roman military tactics. The conquest was completed in 51 BCE with the defeat of the Gallic chieftain Vercingetorix at the Battle of Alesia.
The Roman conquest of Gaul had profound implications for the region. It led to the Romanization of Gaulish society, with the introduction of Roman culture, language, and governance. The integration of Gaul into the Roman Empire facilitated economic growth, urban development, and cultural exchange. However, the conquest also resulted in the loss of Gaulish autonomy and the decline of traditional Celtic culture. The Roman conquest of Gaul is a testament to the transformative power of imperial expansion and its lasting impact on the region.
How Did the Roman Rule Impact Gaul?
The impact of Roman rule on Gaul was significant and multifaceted, altering the region's social, political, and cultural landscape. The Romanization of Gaul brought about profound changes in various aspects of life, including governance, infrastructure, and cultural practices.
• Governance: Under Roman rule, Gaul was divided into provinces, each governed by a Roman-appointed official. The introduction of Roman law and administrative practices streamlined governance and integrated Gaul into the larger Roman Empire. This new system of governance replaced the tribal structures that had previously characterized Gaulish society.
• Infrastructure: The Romans invested heavily in the infrastructure of Gaul, constructing roads, aqueducts, and cities. The development of these networks facilitated trade and communication, contributing to the economic prosperity of the region. Roman cities in Gaul, such as Lugdunum (modern-day Lyon) and Lutetia (modern-day Paris), became important centers of commerce and culture.
• Cultural Practices: Roman culture and language were introduced to Gaul, leading to a blending of Roman and Gaulish traditions. Latin became the dominant language, and Roman customs, art, and architecture influenced Gaulish society. However, elements of Gaulish culture, such as religious practices and local traditions, persisted and blended with Roman influences.
Despite the significant changes brought about by Roman rule, the people of Gaul adapted to this new reality, creating a unique cultural identity that combined Roman and Gaulish elements. The impact of Roman rule on Gaul is evident in the region's enduring legacy and its role in shaping modern European culture.
Cultural Legacy of Gaul
The cultural legacy of Gaul is rich and enduring, reflecting the region's historical significance and its contributions to European heritage. The blending of Gaulish and Roman traditions created a unique cultural identity that has left a lasting impact on art, language, and cultural practices.
• Art and Architecture: The artistic traditions of Gaul were heavily influenced by both Celtic and Roman styles. Gaulish art is characterized by intricate metalwork, ceramics, and sculpture, showcasing the skill and creativity of its artisans. The influence of Roman architecture is evident in the construction of amphitheaters, aqueducts, and temples throughout the region.
• Language: The Latin language introduced by the Romans gradually replaced the Gaulish language, leading to the development of the Romance languages, including French. The linguistic legacy of Gaul is a testament to the region's role in the evolution of modern European languages.
• Cultural Practices: The cultural practices of Gaul were shaped by a combination of Celtic and Roman traditions. Religious beliefs, festivals, and social customs reflect this blend, with elements of both cultures persisting in the region. The legacy of Gaulish culture is evident in the continued celebration of traditional festivals and the preservation of historical sites.
The cultural legacy of Gaul is a testament to the region's historical significance and its role in shaping the cultural landscape of Europe. The enduring influence of Gaulish traditions is a reminder of the region's rich history and its contributions to the development of European culture.
Economy and Trade in Gaul
The economy of Gaul was diverse and dynamic, characterized by agriculture, trade, and craftsmanship. The region's fertile lands and abundant natural resources provided a strong foundation for economic activity, while its strategic location facilitated trade with neighboring regions.
Agriculture was the backbone of Gaulish economy, with the cultivation of crops such as wheat, barley, and oats. The Gauls also engaged in animal husbandry, raising cattle, sheep, and pigs for meat, milk, and wool. The agricultural surplus supported local communities and enabled trade with other regions.
Trade was an essential component of Gaulish economy, with the region serving as a crossroads between the Mediterranean and northern Europe. Gaulish traders exchanged goods such as metalwork, textiles, and ceramics with neighboring regions, contributing to the economic prosperity of the region. The development of Roman infrastructure, including roads and ports, further facilitated trade and economic growth.
Craftsmanship was another important aspect of Gaulish economy, with skilled artisans producing high-quality goods for both local and international markets. Metalworking, pottery, and textiles were among the key industries, showcasing the creativity and skill of Gaulish craftsmen. The economy and trade in Gaul played a crucial role in the region's development and its integration into the Roman world.
Religion and Beliefs of the Gauls
The religious beliefs of the Gauls were deeply rooted in Celtic traditions, characterized by polytheism and a reverence for nature. The Gauls worshipped a pantheon of gods and goddesses, each associated with different aspects of life and the natural world. These deities were often linked to specific locations, such as rivers, forests, and mountains.
Druids played a central role in Gaulish religion, serving as priests, teachers, and advisors. They were responsible for conducting religious ceremonies, interpreting omens, and preserving oral traditions. The Druids wielded considerable influence in Gaulish society, acting as intermediaries between the people and the gods.
Religious practices in Gaul included rituals, sacrifices, and festivals, often held in natural settings such as groves and rivers. These ceremonies were an integral part of Gaulish culture, reflecting the people's connection to the land and their spiritual beliefs. The Roman conquest of Gaul led to the introduction of Roman deities and religious practices, resulting in a syncretism of Celtic and Roman traditions. Despite these changes, elements of Gaulish religion persisted, influencing the development of religious practices in the region.
Gaulish Language and Literature
The Gaulish language was a Celtic language spoken by the inhabitants of Gaul before the Roman conquest. It was closely related to other Celtic languages, such as Gaelic and Welsh, and played a crucial role in the cultural identity of the Gauls. The Gaulish language was used in everyday communication, religious ceremonies, and the transmission of oral traditions.
While written records of the Gaulish language are limited, inscriptions and coins bearing Gaulish text provide valuable insights into the language and its usage. The Gauls also employed the Latin alphabet for writing, particularly after the Roman conquest, contributing to the preservation of Gaulish language and literature.
Gaulish literature was primarily oral, with stories, myths, and songs passed down through generations. These oral traditions were an essential aspect of Gaulish culture, reflecting the values, beliefs, and history of the people. The influence of Gaulish language and literature persisted even after the Romanization of the region, contributing to the development of medieval European literature and the preservation of Celtic heritage.
Where Was Gaul in the Context of the Roman Empire?
In the context of the Roman Empire, Gaul was a crucial region that played a significant role in the empire's expansion and administration. After its conquest by Julius Caesar, Gaul was integrated into the Roman Empire and divided into several provinces, each governed by Roman officials. These provinces included Gallia Narbonensis, Gallia Lugdunensis, Gallia Aquitania, and Gallia Belgica.
Gaul's strategic location made it an essential part of the Roman Empire, serving as a buffer between the Roman territories and the Germanic tribes to the north. The region's fertile lands and abundant resources contributed to the economic prosperity of the empire, while its cities became centers of Roman culture and administration.
The integration of Gaul into the Roman Empire facilitated cultural exchange and the spread of Roman customs, language, and governance. The Romanization of Gaul led to the development of a unique cultural identity that combined elements of both Roman and Gaulish traditions. Gaul's role within the Roman Empire highlights its importance in the history of the region and its lasting impact on European culture.
Decline of Roman Gaul
The decline of Roman Gaul was a gradual process that unfolded over several centuries, marked by internal strife, economic challenges, and external pressures. The weakening of the Roman Empire in the 3rd and 4th centuries CE left Gaul vulnerable to invasions by Germanic tribes, such as the Franks, Vandals, and Visigoths.
These invasions disrupted the stability and prosperity of Roman Gaul, leading to the decline of urban centers and the erosion of Roman authority. The economic challenges faced by the Roman Empire, including inflation and decreased trade, further contributed to the decline of Roman Gaul. The weakening of Roman infrastructure and administration left the region unable to cope with the pressures of external invasions and internal unrest.
Despite these challenges, the legacy of Roman Gaul persisted, with elements of Roman culture, language, and governance continuing to influence the region. The decline of Roman Gaul marked the transition to the medieval period and the emergence of new political entities, such as the Frankish Kingdom, which would shape the future of Europe. The decline of Roman Gaul is a testament to the complexities of historical change and the enduring impact of the Roman Empire on the region.
How Did Gaul Influence Modern Europe?
The influence of Gaul on modern Europe is evident in various aspects of culture, language, and identity. The blending of Gaulish and Roman traditions created a unique cultural legacy that has left a lasting impact on European heritage.
• Language: The Latin language introduced by the Romans in Gaul evolved into the Romance languages, including French, which is spoken by millions of people today. The linguistic influence of Gaul is a testament to the region's role in the development of modern European languages.
• Culture: The cultural practices of Gaul, shaped by a combination of Celtic and Roman traditions, have influenced the development of European culture. Elements of Gaulish culture, such as art, music, and mythology, continue to be celebrated and preserved, contributing to the rich tapestry of European heritage.
• Identity: The legacy of Gaul is reflected in the national identity of modern France, with the region's history and culture playing a significant role in shaping the country's sense of self. The influence of Gaul extends beyond France, contributing to the cultural and historical identity of Europe as a whole.
Gaul's influence on modern Europe is a testament to the region's historical significance and its contributions to the development of European culture and identity. The enduring legacy of Gaul is a reminder of the region's rich history and its role in shaping the modern world.
Archaeological Discoveries in Gaul
Archaeological discoveries in Gaul have provided valuable insights into the region's history, culture, and society. Excavations of ancient settlements, burial sites, and artifacts have shed light on the daily lives, beliefs, and practices of the Gauls.
• Settlements: Excavations of ancient Gaulish settlements have revealed the layout and structure of villages and towns, showcasing the architectural and urban planning skills of the Gauls. These sites provide a glimpse into the social organization and lifestyle of Gaulish communities.
• Burial Sites: The discovery of burial sites has provided important information about Gaulish religious beliefs and burial practices. Grave goods, such as weapons, jewelry, and pottery, offer insights into the social status and cultural values of the Gauls.
• Artifacts: The discovery of artifacts, including pottery, metalwork, and tools, has shed light on the craftsmanship and artistic traditions of the Gauls. These artifacts reflect the skill and creativity of Gaulish artisans and their contributions to the cultural heritage of the region.
Archaeological discoveries in Gaul have enriched our understanding of the region's history and its significance in the ancient world. These findings continue to contribute to the study of European history and the preservation of Gaulish heritage.
Gaul in Popular Culture
Gaul has captured the imagination of artists, writers, and filmmakers, becoming a popular subject in various forms of media. The region's rich history, vibrant culture, and legendary figures have inspired numerous works of literature, film, and art.
• Literature: The story of Gaul and its people has been depicted in various literary works, including historical novels and epic tales. These stories often focus on the bravery and resilience of the Gauls, as well as their encounters with the Roman Empire.
• Film: Gaul has been portrayed in numerous films, often depicting the Gallic Wars and the Roman conquest of the region. These films bring to life the dramatic events and characters of Gaulish history, captivating audiences with their epic storytelling.
• Art: The artistic traditions of Gaul have inspired contemporary artists, who draw upon the region's rich cultural heritage in their work. From paintings to sculptures, Gaul continues to be a source of inspiration for artists around the world.
Gaul's presence in popular culture reflects its enduring fascination and significance in the modern world. The region's history and legacy continue to captivate audiences, contributing to the preservation and celebration of Gaulish heritage.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Where was Gaul located?
Gaul was located in Western Europe, encompassing modern-day France and parts of Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, and Northern Italy.
2. Who were the Gauls?
The Gauls were Celtic tribes that inhabited the region known as Gaul. They were known for their warrior culture, artistry, and complex social structures.
3. What was the significance of Gaul in ancient times?
Gaul was significant due to its strategic location, abundant resources, and cultural influence. It played a key role in the expansion of the Roman Empire and the exchange of ideas and goods.
4. How did the Roman conquest affect Gaul?
The Roman conquest led to the Romanization of Gaul, introducing Roman culture, language, and governance. It also resulted in economic growth and urban development.
5. What is the cultural legacy of Gaul?
The cultural legacy of Gaul includes its art, language, and cultural practices, which have influenced European heritage and modern culture.
6. How did Gaul influence modern Europe?
Gaul influenced modern Europe through its contributions to language, culture, and identity, shaping the development of European heritage and identity.
Conclusion
The history and legacy of Gaul are a testament to the region's significance in shaping the ancient world and its enduring influence on modern Europe. From its strategic location and vibrant culture to its integration into the Roman Empire, Gaul played a pivotal role in the development of European history. The region's rich cultural heritage continues to inspire and captivate, reflecting its importance in the tapestry of human civilization. Understanding where Gaul was and its contributions to history provides valuable insights into the complexities of cultural exchange, conquest, and adaptation. The story of Gaul is a reminder of the resilience and adaptability of its people, whose legacy continues to shape the world today.
The Evolution Of Bon Jovi Tours: A Rock And Roll Phenomenon
Delving Into The Talents Of Actors From Grace And Frankie On Netflix
Masters Of Verse: The Influence Of Argentine Poets

Gaul people Britannica
All Gaul Dickinson College Commentaries